2 Stroke Engine Diagram and Working Principle
Long time ago, two stroke engine become so famous as an engine of vehicle. But now days, the 2 stroke engine is stopped to produce. Its because two stroke engine have bad emissions and bad fuel consumption.
Nevertheles, 2 stroke engine have advantages on power and RPM. The vehicle with 2 stroke engine could running fastly on a limit time.
If you want to know how this work, or want to know the different between four stroke, you can chek this article.
As we learn before on 4 stroke engine diagram, there are four step on an engine cycle.
how about 2-stroke ? are they same ?
of course there are more different. First you can see the name, 2 stroke mean it have only 2 step on a cylce. But, typically this engine have 4 process above though do with only 2 step.
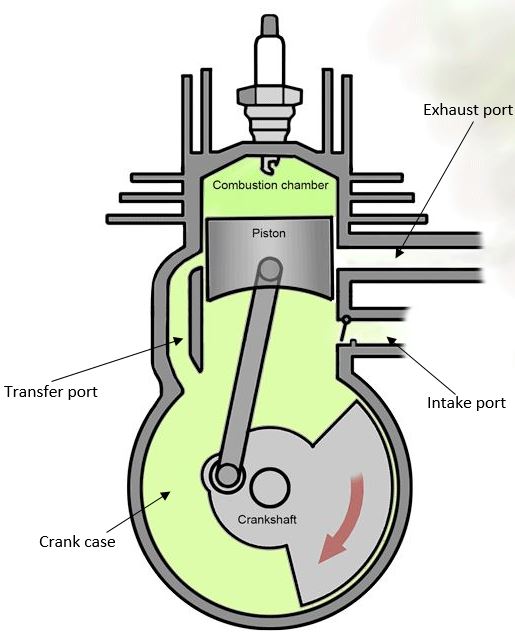
Before we step ahead, you need to understand the important components of two stroke ;
As we said above, the working principle of 2-stroke-engine is different than 4 stroke. The combustion on 4 stroke occurs every 2 rotation of crankshaft while 2 stroke occurs every single rotation. Therefore, the complete process of engine combustion only occurs in two steps.
1. Upward stroke

The first step is the upward stroke, in this step the piston move upward from the BDC (bottom dead center) position to the TDC (top dead center).
When the piston is in the BDC, there are AFM inside the combustion chamber that filled through the previous cycle, the AFM is ready for compression. So that, when the piston moves upward, the piston wall will close two channels, the transfer port and exhaust port. So that the mixture of air and fuel contained in the combustion chamber can be compressed.
On the other side, the piston movement will increase the crank case volume. And as a result there will be a higher vacuum in the crankcase. This vacuum will suck the AFM from the carburetor into the crank case.
2. Downward stroke

Downward strokes or piston moving down step is the movement of the piston from TDC to BDC. This process begins when the spark plug sparking fire, on the end of previous step the piston position is on top which compresses the AFM. So that when the spark plug turns on, the AFM automatically burn.
The result of this combustion is an expansion energy and combustion residual gas, the expansion energy will push the piston to move downward.
When the piston move down, there is transfer process where the AFM inside the crank case will push by piston downward movement. In this case, both the transfer channel and exhaust port are open because the intake channel is covered by a piston wall that moves to the BDC. This will make the air and gasoline mixture in the crankcase move to the transfer port and enter the combustion chamber.
How about residual gasses ?
The residual combustion gas in the combustion chamber will be pushed out by AFM THAT entering through the transfer port. This is also called flushing because the combustion residual gas will be rinsed / released by a new gas that is ready to be compressed.
After the piston rise BDC, the piston will move back to the TDC and compressed the AFM. And its continously happened for the engine running.
From the explanation, we can take a conclucion.
When upward stroke there are 2 process ;
And when downward stroke there are 2 step too ;
It show that 2 stroke engine typically have same procces with 4 stroke engine. Its enough for now, hope usefull for all of we.
Nevertheles, 2 stroke engine have advantages on power and RPM. The vehicle with 2 stroke engine could running fastly on a limit time.
If you want to know how this work, or want to know the different between four stroke, you can chek this article.
2 Stroke Engine Diagram
As we learn before on 4 stroke engine diagram, there are four step on an engine cycle.
- Intake stroke
- Compression stroke
- Combustion stroke
- Exhaust stroke
how about 2-stroke ? are they same ?
of course there are more different. First you can see the name, 2 stroke mean it have only 2 step on a cylce. But, typically this engine have 4 process above though do with only 2 step.
Before we step ahead, you need to understand the important components of two stroke ;

- Crank case, is a crank room used to hold temporary air and fuel mixtures before entering the combustion chamber.
- Combustion chamber, the functions as a place for engine combustion.
- Intake port, serves as the inlet of the air and fuel mixture from the carburetor to the crank case.
- Exhaust port, serves as the outlet of the combustion residual gas from the combustion chamber to the exhaust mufler.
- The transfer port, serves as a connecting channel to transfer AFM (air fuel mixture) between the crankcase and combustion chamber.
As we said above, the working principle of 2-stroke-engine is different than 4 stroke. The combustion on 4 stroke occurs every 2 rotation of crankshaft while 2 stroke occurs every single rotation. Therefore, the complete process of engine combustion only occurs in two steps.
1. Upward stroke

The first step is the upward stroke, in this step the piston move upward from the BDC (bottom dead center) position to the TDC (top dead center).
When the piston is in the BDC, there are AFM inside the combustion chamber that filled through the previous cycle, the AFM is ready for compression. So that, when the piston moves upward, the piston wall will close two channels, the transfer port and exhaust port. So that the mixture of air and fuel contained in the combustion chamber can be compressed.
On the other side, the piston movement will increase the crank case volume. And as a result there will be a higher vacuum in the crankcase. This vacuum will suck the AFM from the carburetor into the crank case.
2. Downward stroke

Downward strokes or piston moving down step is the movement of the piston from TDC to BDC. This process begins when the spark plug sparking fire, on the end of previous step the piston position is on top which compresses the AFM. So that when the spark plug turns on, the AFM automatically burn.
The result of this combustion is an expansion energy and combustion residual gas, the expansion energy will push the piston to move downward.
When the piston move down, there is transfer process where the AFM inside the crank case will push by piston downward movement. In this case, both the transfer channel and exhaust port are open because the intake channel is covered by a piston wall that moves to the BDC. This will make the air and gasoline mixture in the crankcase move to the transfer port and enter the combustion chamber.
How about residual gasses ?
The residual combustion gas in the combustion chamber will be pushed out by AFM THAT entering through the transfer port. This is also called flushing because the combustion residual gas will be rinsed / released by a new gas that is ready to be compressed.
After the piston rise BDC, the piston will move back to the TDC and compressed the AFM. And its continously happened for the engine running.
From the explanation, we can take a conclucion.
When upward stroke there are 2 process ;
- AFM suction
- Compression step
And when downward stroke there are 2 step too ;
- Combustion
- Exhaust gasses removal
It show that 2 stroke engine typically have same procces with 4 stroke engine. Its enough for now, hope usefull for all of we.


